Discover the Top 10 Common Symptoms And Signs Of High Blood Pressure also known as hypertension. Learn about headaches, fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, vision problems, irregular heartbeat, nosebleeds, swelling, and nausea or vomiting. Find out how to detect and manage high blood pressure early for better overall health.
Introduction
High Blood Pressure of Hypertension does not typically show symptoms, but if you have any of the following ten symptoms, you should check your blood pressure immediately or see your doctor.
- Severe Headache
- Nosebleed (Epistaxis)
- Breathlessness
- Tinnitus (Ringing in Ears)
- Sleepiness, Insomnia
- Confusion
- Fatigue
- Excess sweating
- Vomiting
- Blurred vision
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it typically does not cause noticeable symptoms until it reaches a severe stage. However, there are certain signs that may indicate the presence of high blood pressure.
In this article, we will discuss the Top 10 Common Symptoms And Signs Of High Blood Pressure that you should be aware of.
1. Headaches
One of the most common symptoms of high blood pressure is frequent headaches. These headaches are often described as pulsating and occur primarily in the morning. If you experience persistent headaches, it is important to monitor your blood pressure levels.
2. Fatigue
Feeling tired or fatigued even after getting enough rest can be a sign of high blood pressure. When your blood pressure is consistently high, it can put extra strain on your heart, leading to feelings of exhaustion.
3. Dizziness
Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur as a result of high blood pressure. When your blood pressure is too high, it can disrupt the flow of blood to the brain, causing temporary dizziness or fainting spells.
4. Shortness of Breath
High blood pressure can also affect your breathing. If you find yourself frequently short of breath, even during light physical activities, it may be a symptom of high blood pressure. This occurs when the heart has to work harder to pump blood through narrowed arteries.
5. Chest Pain
Chest pain or discomfort can be a warning sign of high blood pressure. This pain is often described as a tightness or pressure in the chest and can be mistaken for a heart attack. If you experience chest pain, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
6. Vision Problems
High blood pressure can affect your eyesight. Blurred vision, double vision, or even loss of vision can occur when the blood vessels in the eyes are damaged due to high blood pressure. If you notice any changes in your vision, it is crucial to consult with an eye specialist.
7. Irregular Heartbeat
An irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia, can be a symptom of high blood pressure. When your blood pressure is elevated, it can disrupt the normal rhythm of your heart, leading to palpitations or a racing heartbeat.
8. Nosebleeds
While nosebleeds can have various causes, they can sometimes be associated with high blood pressure. If you experience frequent or severe nosebleeds, it is important to get your blood pressure checked.
9. Swelling
High blood pressure can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the feet, ankles, or hands. If you notice unexplained swelling, it may be a sign of an underlying health issue, including high blood pressure.
10. Nausea or Vomiting
In some cases, high blood pressure can cause nausea or vomiting. This occurs when the blood vessels in the brain are affected, leading to a feeling of sickness. If you experience persistent nausea or vomiting, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
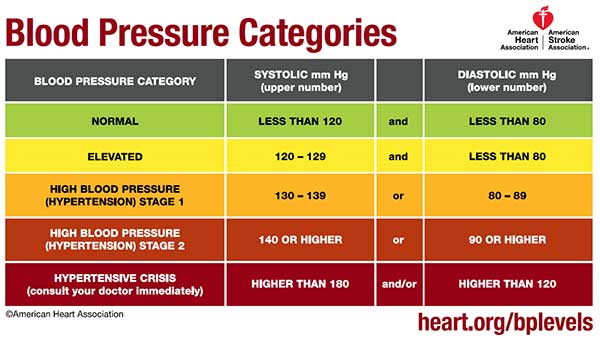
The best way to diagnose HBP is to have it measured. A blood pressure reading, given in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), has two numbers.
- Systolic Blood Pressure (the top number) indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls during heartbeats.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure (the bottom number) indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
Blood pressure measurements fall into four general categories. The American Heart Association’s guidelines are as follows:
- Normal Blood Pressure: A reading of less than 120 (systolic) and 80 (diastolic).
- Elevated Blood Pressure: A reading ranging from 120 to 129 (systolic) and below 80 (diastolic).
- Stage 1 Hypertension: A reading ranging from 130 to 139 (systolic) or 80 to 89 (diastolic).
- Stage 2 Hypertension: A reading ranging from 140 or higher (systolic) or 90 (diastolic).
- Hypertensive Crisis (consult your doctor immediately): A reading higher than 180 (systolic) and/or 120 (diastolic).
What Causes Spikes In Blood Pressure?
- Many different things could trigger a hypertensive crisis. Some of the more common catalysts are: missing a blood pressure medication dosage, heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, or artery rupture.
- You can tell from this list that some issues will be much more critical as far as organ damage, so it is imperative to get to the ER for help.
Conclusion
High blood pressure is a serious condition that requires proper management and treatment. While these symptoms can indicate the presence of high blood pressure, it is important to note that they can also be caused by other health issues. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can accurately diagnose and provide appropriate treatment options.
Remember, regular check-ups and monitoring your blood pressure can help detect and manage high blood pressure early, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health.
It would help if you watched out for chest pain, blurred vision, headache, nausea, pain in the jaw or arm, anxiety, shortness of breath, seizures, confusion, or a general lack of responsiveness. Coupled with a high blood pressure reading, any of these are causes for emergency response.



